Top articles
- High-purity 99.7% alumina ceramics helpful to semiconductor manufacturing technology
- Alumina Ceramic Grinding Balls: High-Efficiency Solutions for Industrial Grinding
- How to Select Suitable Wear-Resistant Ceramic Lining Tiles in the Mining Industry
- Advantages of Ceramic Rubber Composite Liners in Industrial Applications
- How to Install Alumina Ceramic Liners for Long-Lasting Adhesion?
- 99% alumina bulletproof ceramics are the preferred materials for protective devices
- Alumina Ceramic Substrates:Characteristics,Advantages,Disadvantages,and Applications
- Why do alumina industrial ceramics wear out?
- The reason of abrasion resistant ceramic tiles falling off when pasted on equipment
- Seven aspects of advantages & applications of alumina ceramic substrates
Latest articles
- High-purity 99.7% alumina ceramics helpful to semiconductor manufacturing technology
- Alumina Ceramic Grinding Balls: High-Efficiency Solutions for Industrial Grinding
- How to Select Suitable Wear-Resistant Ceramic Lining Tiles in the Mining Industry
- Advantages of Ceramic Rubber Composite Liners in Industrial Applications
- How to Install Alumina Ceramic Liners for Long-Lasting Adhesion?
- Welcome to EXPOMIN 2025
- 99% alumina bulletproof ceramics are the preferred materials for protective devices
- Alumina Ceramic Substrates:Characteristics,Advantages,Disadvantages,and Applications
- Why do alumina industrial ceramics wear out?
- Chemshun Ceramics Chinese New Year Holiday Notice
Your browsing history

Advantages of Ceramic Rubber Composite Liners in Industrial Applications
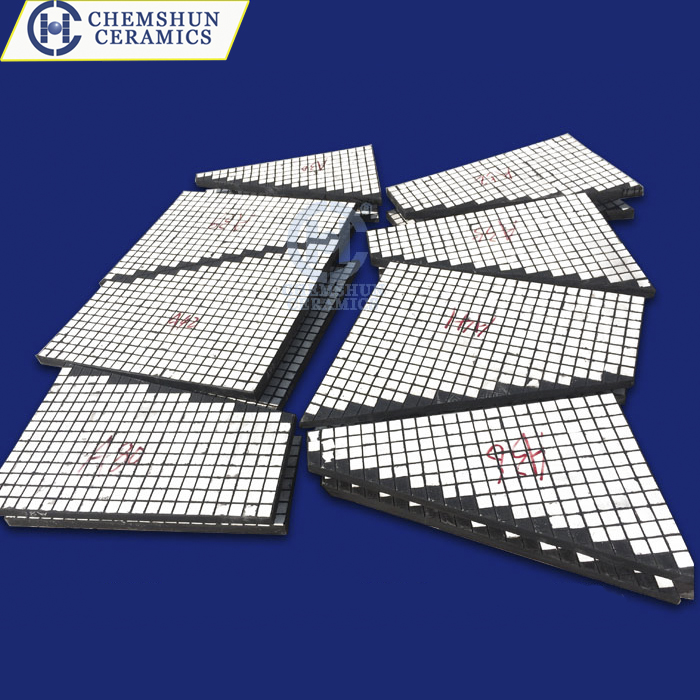
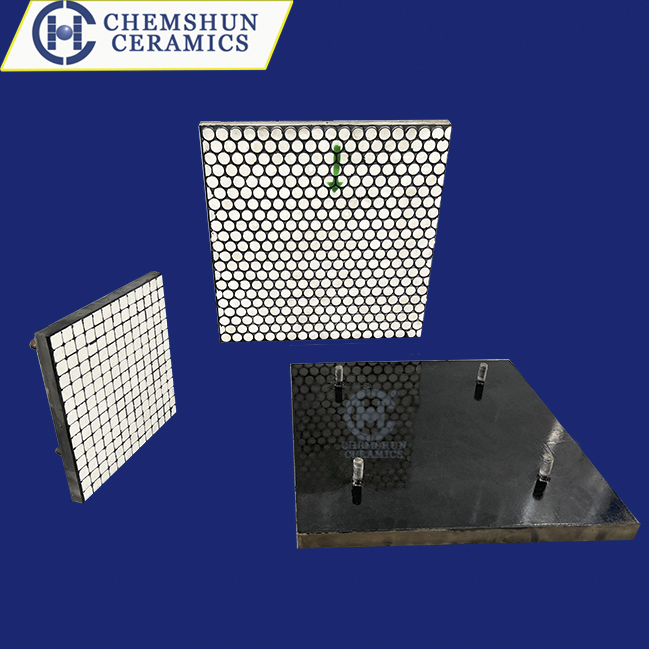
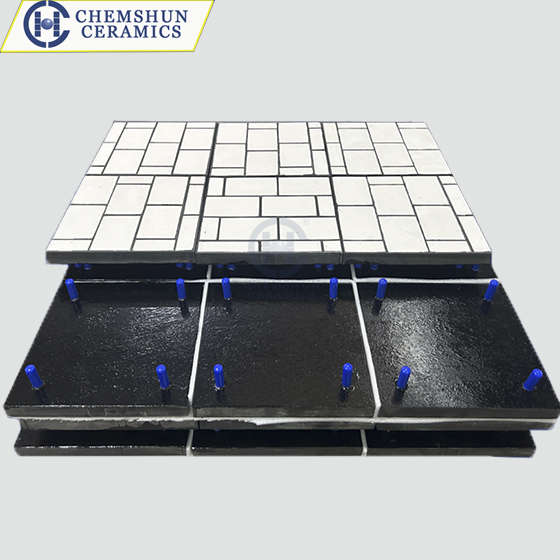
Ceramic rubber composite liners, as high-performance composite materials, integrate the high hardness and wear resistance of ceramics, the flexibility and shock absorption of rubber, and the easy installation of steel plates. These liners demonstrate significant advantages in various industrial applications.
1. Superior Wear Resistance
Ceramic rubber composite liners combine the high hardness and wear resistance of ceramic materials with the elasticity and toughness of rubber. The ceramic surface layer utilizes high-hardness, ultra-wear-resistant alumina ceramic material, with a hardness exceeding HRA85, offering 271.5 times the wear resistance of manganese steel. This effectively mitigates material abrasion and substantially extends equipment service life. In industries such as steel manufacturing and mining, where heavy wear is prevalent, ceramic rubber composite liners excel as an ideal solution for protecting equipment.
2. Outstanding Impact Resistance
The rubber substrate provides excellent flexibility and vibration damping, enabling effective absorption and dispersion of impact forces. When equipment is subjected to large material impacts, the rubber layer acts as a buffer, preventing direct impact-induced fractures in the ceramic layer. This superior impact resistance makes ceramic rubber composite liners highly advantageous in high-impact environments like hoppers and chutes.
3. Excellent Corrosion Resistance
The inherent corrosion resistance of ceramic materials ensures robust protection against chemical erosion. Consequently, ceramic rubber composite liners perform exceptionally well in industries such as petrochemicals and power generation, safeguarding equipment from corrosive damage.
4. Easy Installation and Maintenance
Ceramic rubber composite liners are designed for straightforward installation and maintenance. The steel plate backing includes pre-drilled bolts for easy attachment to equipment shells. When liners reach their wear limit, they can be quickly replaced, minimizing downtime and reducing maintenance costs.
5. Broad Application Scope
Thanks to their exceptional performance, ceramic rubber composite liners are widely adopted across multiple industries. They effectively withstand material abrasion and impact, protecting equipment from damage and enhancing operational efficiency. These liners play a critical role in material handling systems within mining, metallurgy, power, and chemical industries.