Top articles
- Alumina Ceramic Substrates: The Invisible Backbone of Modern Industry
- 99% Alumina Ceramic: The Superior Choice for Bulletproof Armor Materials
- Analysis of the Characteristics of Rubber Ceramic Composite Liners
- Excellent Ceramic Material—ZTA Toughened Alumina Ceramic
- Characteristics of Wear-Resistant Alumina Ceramic Tubes
- Wear resistant ceramic pipes for pneumatic conveying of lithium batteries
- What should be paid attention to when choosing to use wear-resistant ceramic linings
- The difference between wear-resistant ceramic pipes and traditional steel pipes
- Precautions for the application of wear-resistant ceramic glue
- Application of wear-resistant ceramic pipes
Latest articles
- Alumina Ceramic Substrates: The Invisible Backbone of Modern Industry
- Chemshun High-Performance Ceramic Substrate Production Line Kiln Officially Ignited and Put into Operation!
- 99% Alumina Ceramic: The Superior Choice for Bulletproof Armor Materials
- Analysis of the Characteristics of Rubber Ceramic Composite Liners
- Excellent Ceramic Material—ZTA Toughened Alumina Ceramic
- Characteristics of Wear-Resistant Alumina Ceramic Tubes
- Wear resistant ceramic pipes for pneumatic conveying of lithium batteries
- What should be paid attention to when choosing to use wear-resistant ceramic linings
- The difference between wear-resistant ceramic pipes and traditional steel pipes
- Precautions for the application of wear-resistant ceramic glue
Your browsing history

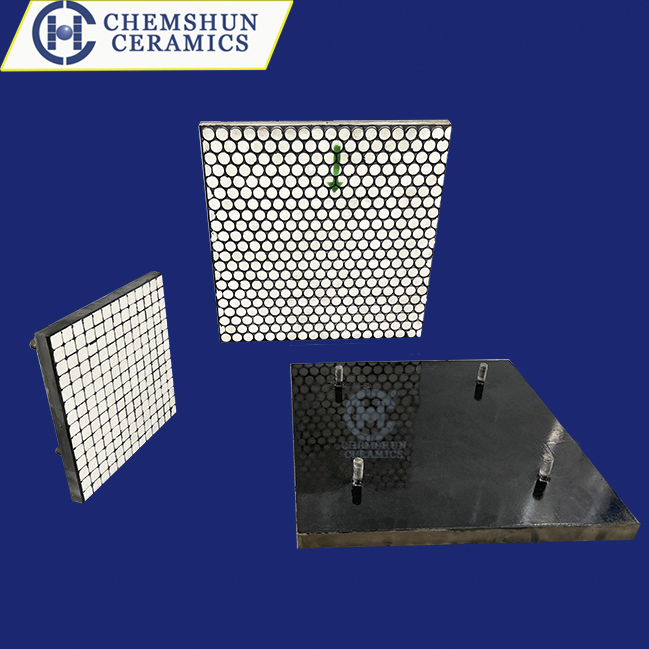
Analysis of the Characteristics of Rubber Ceramic Composite Liners
Rubber ceramic composite liners are high-performance materials that combine the excellent wear resistance of alumina ceramics with the elastic cushioning properties of rubber. They are widely used in high-wear scenarios across heavy industries such as thermal power, steel, mining, and cement. Below is a detailed breakdown of their core characteristics:
1. Exceptional Wear Resistance
Alumina ceramic, as the primary material of the liner, typically contains ≥92% aluminum oxide (Al2O3), with high-purity variants reaching over 95%. Through high-temperature sintering (1700°C), the ceramic layer achieves a Rockwell hardness (HRA) of 85–90, second only to diamond. Its wear resistance far exceeds traditional metals—for example, it is 266 times that of manganese steel and 171.5 times that of high-chromium cast iron. This property extends the service life of equipment like coal conveying systems, coal mills, and hoppers by over 10 times under prolonged material abrasion.
2. Outstanding Impact Resistance and Cushioning Performance
The rubber layer, tightly bonded to the ceramic through vulcanization, provides excellent impact resistance. The elasticity of rubber effectively absorbs the impact force from large falling materials (e.g., ores, coal), reducing the risk of ceramic breakage. For instance, even when bent 360°, the ceramic remains intact. Additionally, the rubber layer minimizes noise and vibration during material transportation, enhancing operational stability.
3. Resistance to Extreme Temperatures and Chemical Corrosion
Temperature Resistance: The ceramic layer withstands long-term exposure to 0–250°C, while specially formulated rubber retains elasticity between -50°C and 100°C (heat-resistant variants up to 250°C), preventing aging or brittleness.
Chemical Resistance: The ceramic resists weak acids, alkalis, and chemical media, making it suitable for corrosive environments in chemical and metallurgical industries.
4. Lightweight and Easy Installation
With a density of 3.5–3.9 g/cm³ (half that of steel), alumina ceramic significantly reduces equipment load. The modular design (e.g., 300×300 mm or 500×500 mm) allows cutting and shaping for installation on irregular surfaces, minimizing gaps and material clogging risks.
5. Cost-Effectiveness and Longevity
The rubber layer has a service life of ≥15 years, and the ceramic layer lasts over 10 years under normal conditions, drastically reducing maintenance downtime and replacement costs. For example, in power plant coal systems, these liners extend coal mill lifespans by 2–3 years.
Application Scenarios
Energy Industry: Coal conveying pipelines and coal mill liners in thermal power plants.
Metallurgy: Blast furnace bunkers, sintering plant chutes.
Mining & Cement: Crusher chutes, classifier liners.
Chemical & Ports: Corrosive media pipelines, port unloading equipment.
Rubber ceramic composite liners address the limitations of traditional materials in heavy-load, high-impact, and corrosive environments by leveraging alumina ceramic’s extreme wear resistance and rubber’s elastic buffering. Advanced manufacturing techniques (e.g., isostatic pressing, ultra-high-temperature sintering) and scientific structural design further enhance their performance, making them the preferred solution for industrial wear protection.